The global combined demand of all biodegradable plastics(PLA, Starch based plastics, PHA, and all other combined together) in 2018 was estimated to be around 631 kilo tons, with PLA leading the consumption with more than 42.7% market shares. Starch based plastic followed with 42% market share, while the third biggest biodegradable plastic was PHA with a market share of around 2.3%. All other types of biodegradable resins like Polycaprolactone(PCL), polybutylene succinate (PBS), and Regenerated Cellulose resin together trailed with a share of 4.8%. All other biodegradable plastics accounted for around 8.3% of the total demand in 2018.
The growth of the global biodegradable plastics consumption will strongly depend on the economic growth as well as the substitution of biodegradable bioplastics for other traditional materials. The growth rate will be very high in most of regions of the world. Most of the countries in the world will witness double-digit growth for almost all of the biodegradable plastics. It is forecast that mature economies like Western Europe and Japan will also witness much higher growth in comparison to conventional plastics where growth rates are lower to marginal. The countries in Asia-Pacific region including China, Taiwan, Thailand, and India will witness higher than global average growth during the forecast period till 2025.
The biodegradable plastics growth in the mature economies to an extent will depend on the future improvements and advancements expected in the PLA and Starch blend process and other advancements in the technologies. It will also depend on the regulations and minimize the price in comparison to other commodity plastics. It is expected that any technology developments for producing a lower-priced range of products and different grades will increase product consumption in the market.
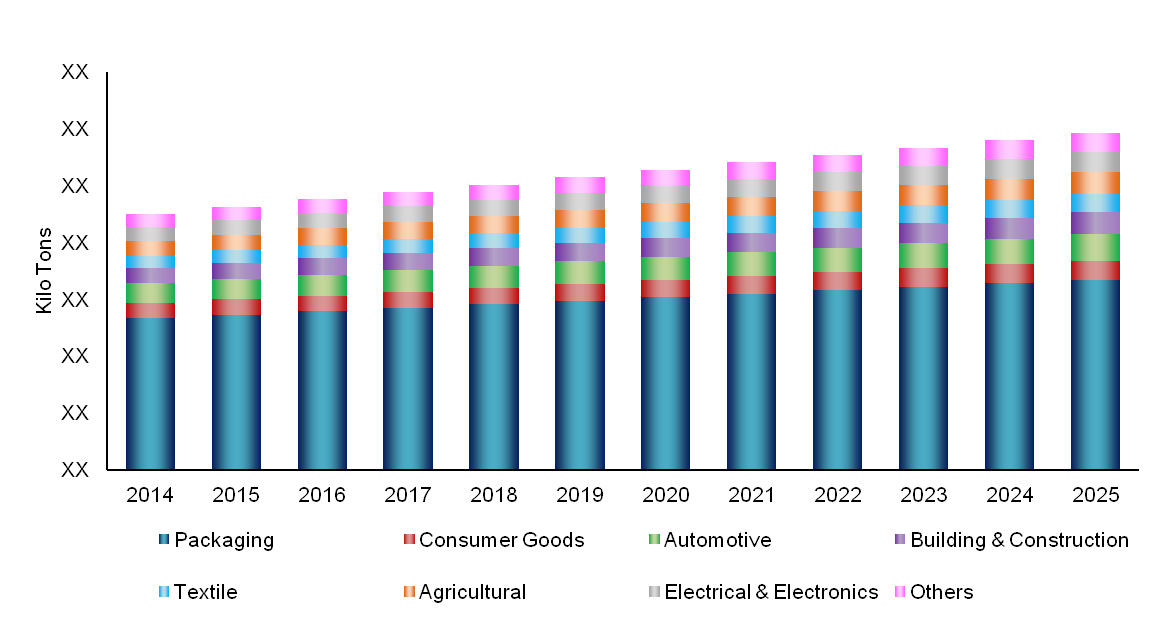
The global market has grown at an average of 15.1% from 2015 to 2018 mainly due to strong demand from biodegradable plastic applications like packaging, consumer goods, agricultural applications, and automotive in Western Europe and Asia-Pacific region. The growth of the global consumption will strongly depend on the economic growth as well as the other dynamics in the packaging that also include bags, automotive applications, and fluctuations in consumer spending.
Biodegradable polymer growth is not closely related to GDP growth as like in the consumption of the commodity polymers which are directly correlated to economic growth. The biodegradable plastic growth is indirectly related to a lot of factors like government initiatives, regulations and development of a country, purchasing power, and awareness. On a global level, the combined growth of all biodegradable plastics taken together has mostly been 3 – 4 times higher than the global GDP except for the 2008 – 2009, economic recession.
During the forecast period, PLA and Starch blends are expected to grow at a CAGR of 15% and 12.3% with the increasing importance of developing economies and the availability of low-feedstock. All other biodegradable plastics are expected to grow at exceptionally high rates, mostly owing to a low base and opportunity for high penetration.
Biodegradables are used in various applications, primarily used in packaging applications like hand-bags, loose filing, and other packaging items. Collectively, these uses make up approximately 63.3% of global biodegradable plastics use. Amongst all other applications, the use of biodegradable plastics in consumer goods is predominant. It accounts for around 12.6% of global biodegradable plastics demand.
The percentage of biodegradable plastics used for agricultural applications is around 9.2%. The demand for PLA is higher in developed countries such as Japan, Taiwan, USA, and Germany while its penetration level is comparatively low in countries like China, India,other Asia-Pacific as well as some countries in Western Europe. In China, fully& partially degradable plaststrarch material (PSM), and polybutyrate (PBAT) are the major ones followed by PLA. Unlike the engineering plastics sector in China, only around 10 – 15% of the companies have JV with foreign MNCs while others are mostly domestic producers.
Western Europe, USA, and Japan have the advantage of technology and regulations while in China it is the move towards minimizing the export dependency and also on account of lower cost of production. The additions of PLA, starch-based plastic, and other capacities are not likely to cause a significant decline in operating rates as strong growth from China and Europe will push the utilisation rates higher for all major export oriented plants. Some of the Chinese companies produce most of the biodegradable polymers only after receiving the order. Historically the demand has not outstripped the capacity additions; however, during the forecast period, there may be surplus capacity, if all the announced projects are online as decided.