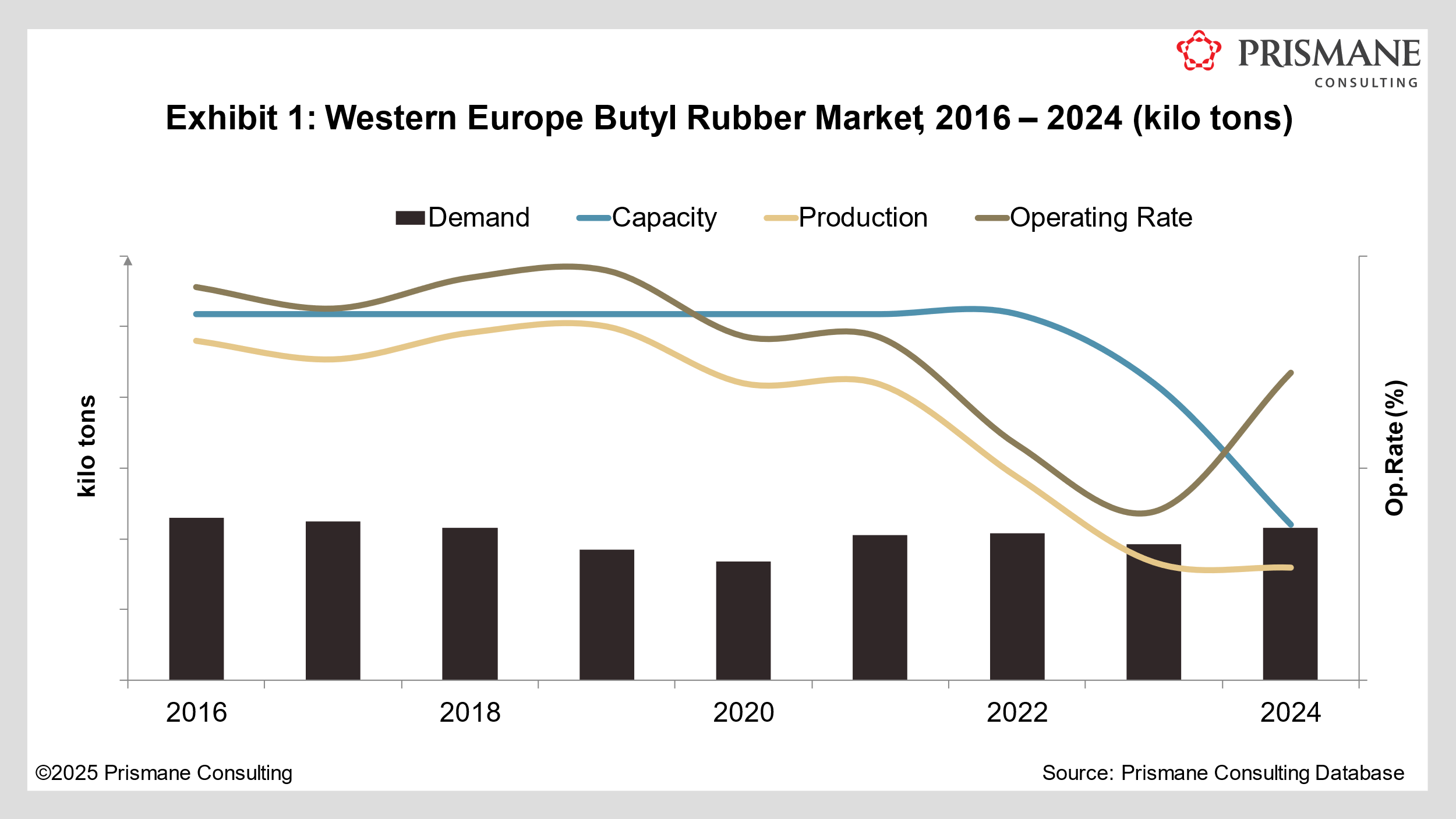
Europe: Little Glimmer of Hope So Far
Synthetic rubber market had a challenging 2024, underpinned by mounting costs, shifting dynamics, and restructuring efforts. While rising feedstock costs has been a concern in the industry for several years now, market participants were especially unprepared for the downturn observed during the “black swan” years – from COVID-19 pandemic to Russia-Ukraine war, high interest rates, recessions, to conflict in the Red Sea. While other regions have managed to somewhat offset those headwinds since then, Europe continues to struggle.
High inflation rates resulting from the events weakened sentiment in the automotive sector. With the industry being the biggest outlet for synthetic rubber – constituting for more than half the total volumes – demand remained tepid. Other factors, such as overcapacity, further weighed on volumes, with output for feedstocks like butadiene, ethylene, and propylene remaining robust without a proportional uptick in demand.
Escalating feedstock prices, shipping disruptions, geopolitical uncertainties, and an overall weaker demand scenario have left European producers with contracted margins, forcing them to engage in restructuring efforts. These include Versalis (subsidiary of Eni) slashing its butadiene supply and phasing out cracking capacities in Italy.
In December 2023, the company announced the shutting down of its Grangemouth site in UK, producing 105 kilo tons/year of polybutadiene and 70 kilo tons/year solution styrene butadiene rubber (sSBR). “Declining sales, increasing costs, and worsening conditions of the elastomers market” were blamed for the permanent closure. UK also saw SABIC shuttering its 100 kilo tons/year butadiene facility at Wilton Teesside in 2020. In 2017, INEOS idled a 70 kilo tons/year butadiene at Grangemouth. In 2020, Trinseo ceased operations at its polybutadiene rubber (PBR) facility at Schkopau, Germany. Citing “unsustainable market due to unpredictable costs”, Synthos permanently shut down its 100 kilo tons/year emulsion SBR (eSBR) facility at Kralupy, Czech Republic. Part of the reason behind some of these closures is also the rise of electric vehicles and the global shift toward decarbonization, which pressured financials.
Asia: Growth Amidst Challenges
Asia’s response to the shifting rubber landscape has been mixed. On one hand, the region continues to see strong production levels, especially in China, which recently returned to pre-COVID production peaks. However, challenges persist. Some producers are closing plants that have failed to meet expected performance levels, while others have been forced to scale back production due to low margins and weak demand.
The ongoing geopolitical tensions, particularly the conflict between Russia and Ukraine, have disrupted global supply chains, adding further complexity to rubber production. The aftermath of these tensions has opened up new opportunities in Eastern and Western Europe, with certain companies acquiring and ramping up production at previously shuttered sites.
USA: Resilient & Well-Oriented Volumes
While Europe and parts of Asia face closures and restructuring, the U.S. has managed to exhibit some positive growth, particularly in the automotive sector. Despite high inflation rates, the U.S. economy has remained relatively stable, a factor that has helped stabilize demand for synthetic rubber. This is largely due to the country's diverse and resilient economy, which has seen a strong recovery in consumer spending and industrial production, especially in the automotive and mobility sectors. The U.S. has also benefited from its lower feedstock costs, which have helped some domestic producers remain competitive globally.
However, even in the U.S., there are challenges. High interest rates have caused some strain on durable goods consumption, and the automotive market has yet to return to its pre-COVID levels. As a result, synthetic rubber producers in the U.S. remain cautious, and the ongoing inflationary pressure continues to cast a shadow over the outlook.
Looking Ahead
The synthetic rubber industry is currently in a transition and restructuring phase. With fluctuating global markets, companies are being forced to adjust their strategies to stay afloat. The road to recovery will likely be slow and gradual, and it remains uncertain when – or if – the market will return to a more stable, pre-pandemic state.