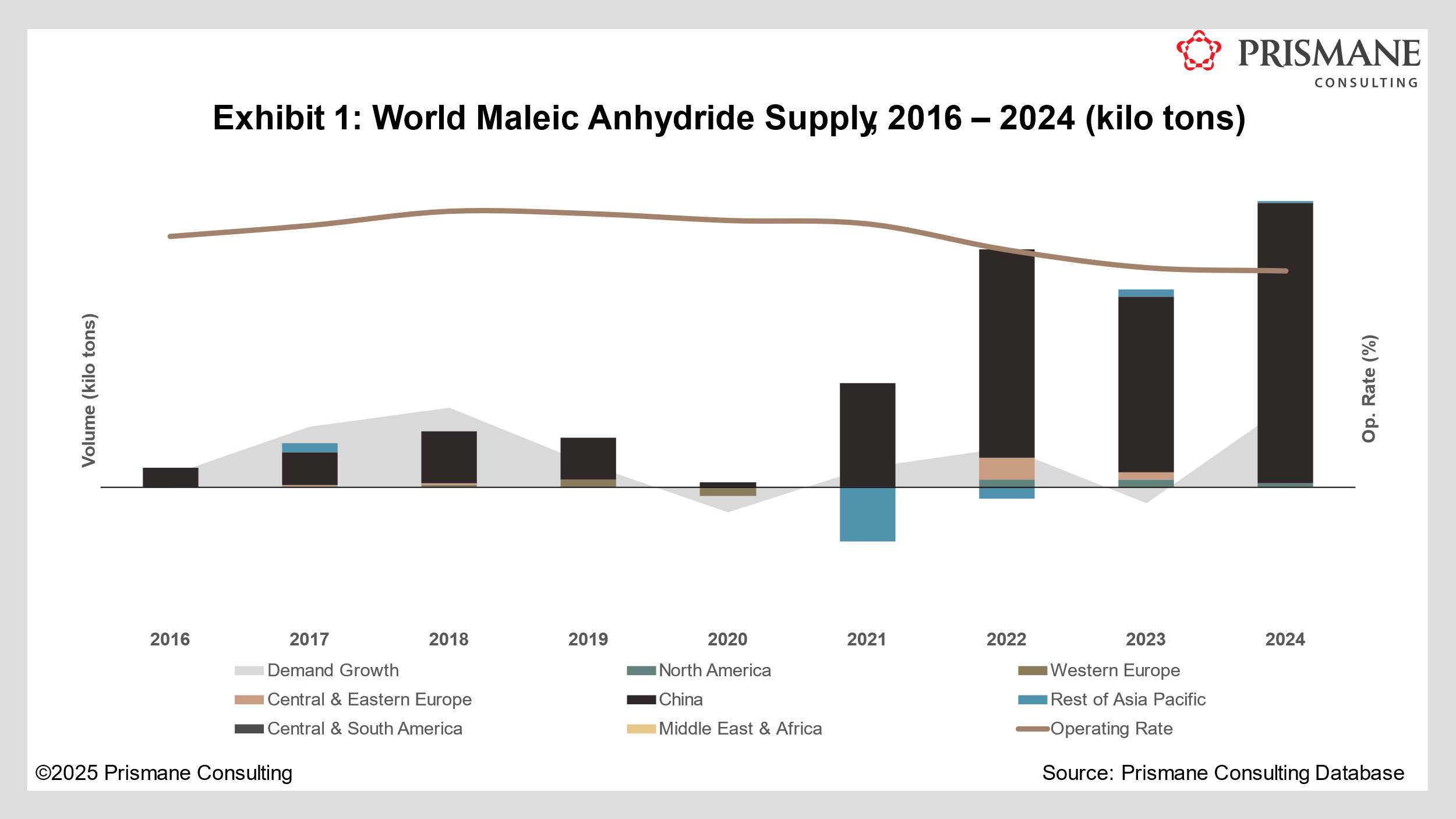
Maleic anhydride markets continued to witness persistent weakness into 2024 amid a slowdown in key sectors like automotive, electronics, and construction. Both 2022 and 2023 saw softened demand amid geopolitical issues and a recessionary environment. Europe was arguably the hardest hit during this period, with weaker demand across the automotive and construction sector and higher than usual destocking amid supply constraints and high feedstock costs following the onset of the Russia- Ukraine war. Both construction and Do-it-yourself (DIY) markets saw contracted volumes amid slow activity and interest rate hikes. Currency effects were also a net negative for maleic anhydride market participants in Europe, with both the US Dollar and the Chinese Yuan appreciating considerably.
A key contributor to the demand lull in Europe was its construction sector, which saw architectural coating volumes failing to register an uptick even during the peak season. Elevated mortgage rates also pressured the residential segment, impacting volumes. Headwinds from the sector were only partially offset by some pockets of growth in the automotive industry, thanks to production rebound and easing supply bottlenecks. Maleic anhydride serves as a key raw material in the production of unsaturated polyester resins (UPR), used subsequently in automotive applications.
On the supply side, the influx of cheaper imports weighed on European margins, prompting output cuts and price slashes.
Meanwhile, China bought onstream significant amounts of new capacity, only to find its own demand to be tepid, forcing some projects to be postponed. The additional supply that came online, however, pressured global margins regardless. Companies producing maleic anhydride from both benzene and butane suffered; plants based on the former were forced to cease operations momentarily due to high benzene prices, while butane-based plants saw operating levels slipping to the 50s. Nevertheless, China added nearly 1.5 million tons of new maleic anhydride capacity in 2024. Another 2.5 million tons of supply is, meanwhile, scheduled in the next 2-3 years (see Exhibit 1). Most of these plants, however, will be downward integrated to produce 1,4-butanediol (BDO). While this might seem attractive, it is not the best investment at the moment, given the low prices for BDO versus its high production costs.
Maleic anhydride market in the USA fared relatively better than Europe during 2022-2023, underpinned by easing inflation, rebounding consumer confidence, and well-oriented construction volumes. On the other hand, demand was much softer in Latin America, which grappled with soaring inflation and rising political tensions.
With an oversupplied market, China’s net exports have grown sequentially in recent years. Much of these excess volumes have flown to other countries in Asia and to Europe, at discounted prices. While export volumes did fall in 2023 owing to conflicts in the Red Sea and increased exports from Sibur’s 45 kilo tons/year plant in Russia, they managed to rebound to its highest recorded levels in 2024.
Concluding Thoughts
Overall, maleic anhydride demand remained flat without any meaningful respite in 2024. Logistics, although better off than 2023, continued to lead to increased freight costs and lengthen lead times. The corresponding rebound was weak, and volumes generally remained flat. UPR continues to suffer, mainly owing to weak housing starts and new car registrations. Asian imports did not wreak as much havoc in the West, as high shipping costs rendered foreign material uncompetitive and local supply to be prized.
Supply glut in China, coupled with a weaker demand scenario with the country’s real estate woes, has left operating rates there to fall significantly, and producers are forced to sell volumes at less-than-fair value. Compared to the West, here prices are still significantly elevated. Chinese manufacturers are unable to capitalise on the arbitrage opportunities, primarily owing to high transportation costs and shipping delays, leaving consumers to instead procure local supplies. With easing supply chains, however, and China continuing to add significant capacities, this will likely exert even more pressure on global margins. In this context, EU volumes are more prone to be injured since USA imports negligible cargoes from China, and if at all, will be largely discouraged by the imposed tariffs.
Excess global supply has caused key manufacturers to cease operations and some to permanently shutter plants. YPF, which was the sole maleic anhydride manufacturer in Argentina, closed its 17.5 kilo tons/year facility at Ensenada at the end of 2024. In Taiwan, Nan Ya Plastics Corp. paused operations at its 60 kilo tons/year facility at Mailiao in Q4 2024, blaming “difficult market conditions”.
With its massive oversupply, China will likely take up market shares of other Asian exporters to the West as they engage in price wars. Market participants in Europe remain pessimistic on improvement in 2025, while Chinese producers have pinned their hope on Government stimulus. In the USA, participants remain uncertain of the market scenario with the recently inaugurated Trump government’s tough stance on tariffs.