Polyisobutylenes (also known as polyisobutenes or PIB) are vinyl polymers typically produced through the polymerization of isobutylene. Usually ranging from a few hundreds to a few millions of molecular weights, PIBs come in various forms. Depending on molecular weight, PIBs are categorized into low, medium, and high molecular weight types. Within the low molecular weight category, PIBs are further split into conventional (C-PIB) and highly reactive (HR-PIB) types. HR-PIBs are characterized by reactive terminals, making them suitable for applications that require high chemical reactivity, such as crosslinking, curing, and bonding. In contrast, conventional PIBs have fewer reactive terminals and are generally used in less demanding applications.
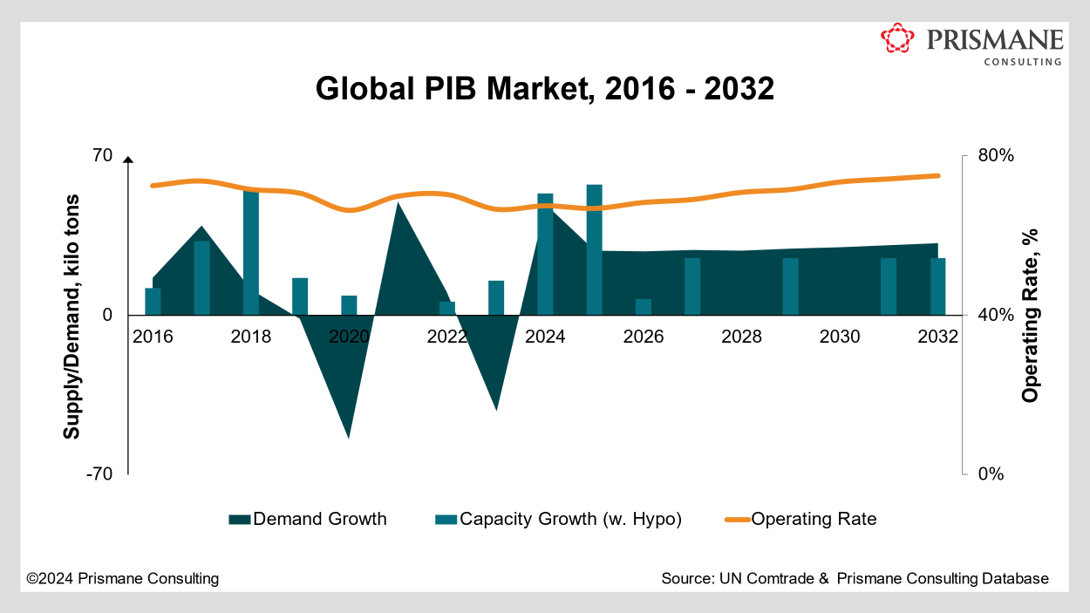
PIB is a concentrated market, with around 1.45 million tons of global capacity (including medium and high molecular weight PIBs) in 2024 residing in 12 countries and dominated by a select few major players. The top six producers – USA, South Korea, China, Germany, France, and Belgium, collectively control more than 80% of the world's supply. Key manufacturers include BASF, Lubrizol, DL Chemical (formerly Daelim Industrial), Infineum (joint venture between Shell and ExxonMobil), Chevron Oronite, and TPC Group (formerly Texas Petrochemicals). More than 40% of global capacity is concentrated in Asia Pacific, residing in South Korea, China, India, Japan, and Malaysia. USA and Western Europe (held by Germany, France, and Belgium) follow Asia Pacific as the second largest producer, each holding a market share of nearly 28%. The remaining 5% share is collectively represented by Brazil, Argentina, and Russia.
In the last two decades, PIB supply in North America has declined – capacity has declined by more than 150 kilo tons since 2000. These included closures from bp, Asia Pacific, meanwhile, has seen robust supply growth, grown more than 500 kilo tons over the same period.
Since 2016, more than 150 kilo tons of PIB supply has hit the market, nearly 95% of its in Asia Pacific. These include capacity additions in South Korea, Malaysia, China, and India. Nearly 100 kilo tons of new supply is slated to add over in the near-term, including new swing C-PIB/HR-PIB plant from Saudi Aramco, TotalEnergies & Daelim JV in Saudi Arabia, and medium mol. wt. PIB expansion by BASF in Ludwigshafen, Germany.
There are several demand outlets for polyisobutylenes, although lubricating additive manufacturing dominates the global demand, representing nearly half of the total volumes. Together with fuel additives and adhesives & sealants, the three applications constitute for three-fourths of world’s consumption. Other uses for PIB include 2-stroke engine oils, industrial lubricants, metalworking fluids, chewing gums, roofing & wire coatings, mining explosives, cosmetics, and stretch films. Global PIB consumption totalled a little over a million tons in 2024, with Asia Pacific representing more than one third of the consumed volumes, followed by North America and Western Europe. Together, the three regions make up for nearly 95% of the demand.
Demand for PIBs has grown at an annual average rate of 0.9% in the last decade. On the back of growth in Asia Pacific Prismane Consulting anticipates global volumes to grow at a 2.6% average rate over the forecast. With lubricating additives constituting half of the global PIB consumption pie, its volume growth is closely linked to the demand for finished lubricants.
While the demand for both low mol. wt. PIBs is split nearly equally between C-PIB and HR-PIB, volumes for the latter are poised to grow at a faster rate than the former over the forecast, driven by growing demand for additives. Standards set by the International Lubricants Standardization and Approval Committee (ILSAC) play a key role in shaping this trend, as new specifications require advanced additives that HR-PIBs are better suited to provide. The introduction of the GF-6 standard in 2020 significantly boosted HR-PIB demand that year. In contrast, growth in C-PIB volumes will be primarily supported by its use in greases and gear oils. Demand in 2-stroke engines (a key outlet) is projected to decline, as the market increasingly shifts towards four-stroke engines in two-wheelers.