A sustainable future can be achieved through various means, but achieving net-zero emissions is of paramount importance. Net-zero emissions entail a delicate equilibrium between the amount of greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere and the amount removed from it.
One of the most effective strategies to curtail greenhouse gas emissions is the adoption of hydrogen, particularly green hydrogen. Green hydrogen is harnessed through renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. Hydrogen exhibits remarkable versatility as an energy source, serving a multitude of applications such as power generation, steel production, transportation, and diverse industrial sectors.
Substituting fossil fuels with hydrogen in these applications has the potential to significantly slash greenhouse gas emissions. Hydrogen, in addition to its applications, acts as an adaptable energy carrier, facilitating the storage and transport of renewable energy. This renders it an invaluable tool in the integration of renewable energy into the power grid and the decarbonization of the transportation sector.
Nonetheless, its worth noting that the production of hydrogen itself is energy intensive. Therefore, a holistic approach to emission reduction should encompass the following:
- Implementing carbon capture techniques in current hydrogen production processes - often referred to as Blue Hydrogen.
- Relying on renewable energy sources for hydrogen production through water electrolysis - known as green hydrogen.
- Embracing renewable energy sources across transportation and industrial sectors.
- Exploring alternatives to carbon-intensive processes.
- Maximizing the utilization of renewable energy sources.
- Relying on renewable energy sources for hydrogen production through water electrolysis - known as green hydrogen.
- Embracing renewable energy sources across transportation and industrial sectors.
- Exploring alternatives to carbon-intensive processes.
- Maximizing the utilization of renewable energy sources.
Net-Zero Targets
The Paris Agreement stands as a legally binding international treaty on climate change. It gained approval from 196 parties at the UN Climate Change Conference (COP21) in Paris, France, on December 12, 2015, and became operational on November 4, 2016. The primary objective of the Paris Agreement is to constrain global warming to levels well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial benchmarks and endeavor to limit the increase to a mere 1.5 degrees Celsius.
As of 2023, an impressive 194 parties have joined the Paris Agreement, encompassing significant players like the United States, China, the European Union, and India. Collectively, these four nations are responsible for approximately half of the world s greenhouse gas emissions. Notably, all major countries have committed to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050, accompanied by comprehensive policies and targets for 2030 and 2050 aimed at reducing their emissions.
Net-Zero Targets, By Country
China:
China has pledged to achieve net-zero emissions by 2060. This is a significant commitment considering China s status as the world s largest emitter of greenhouse gases.
United States:
The United States has set a target to attain net-zero emissions by 2050. This commitment was made by the Biden administration as part of its rejoining the Paris Agreement.
European Union:
The European Union has committed to becoming climate-neutral by 2050. It aims to achieve this goal by implementing the European Green Deal and various associated policies and initiatives.
Japan:
Japan has announced its intention to reach net-zero emissions by 2050. This commitment, made by Prime Minister Yoshihide Suga, represents a significant shift in Japan s climate policy.
United Kingdom:
The United Kingdom has established a legally binding target to achieve net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. This goal was set forth under the Climate Change Act of 2008.
France:
France has set a net-zero target for 2050 as part of its Energy Transition for Green Growth Act. The country aims to achieve carbon neutrality and reduce its greenhouse gas emissions to net zero by this date.
Germany:
Germany has committed to reaching net-zero emissions by 2045. The country's ambition is to transition to a fully decarbonized economy across all sectors, including energy, transport, and industry, by this target year.
Canada: Canada has set a net-zero emissions target for 2050. The country aims to achieve this by implementing strengthened climate policies, investing in renewable energy, and transitioning to a clean economy.
Australia:
Australia has not yet established a national net-zero target, although various states and territories have made commitments to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050 or sooner.
New Zealand:
New Zealand has legislated a net-zero target for 2050 under the Zero Carbon Act. The country s objectives include reducing greenhouse gas emissions to net zero and decreasing methane emissions from agriculture by 24-47% by 2050.
Some countries are still in the process of formulating their net-zero strategies. These targets and commitments are subject to change as countries reassess and update their climate action plans. Countries have also developed hydrogen strategies to achieve net-zero emissions, which include investments in installing green hydrogen capacities and capturing carbon dioxide in existing facilities.
The Role of Hydrogen in Achieving Net Zero
Hydrogen can play a significant role in achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. It is a versatile energy carrier that can be used to decarbonize many sectors of the economy, including industry, power generation, transportation, buildings, and more.
Hydrogen can be employed to produce heat and electricity for industrial processes such as steelmaking, cement manufacturing, and fertilizer production. It can also be used to generate electricity in gas turbines or to store renewable energy for later use. Hydrogen powers fuel cell vehicles, producing zero emissions at the tailpipe, and can be used for heating buildings and providing hot water.
Hydrogen can be produced in various ways, but the most sustainable methods utilize renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power. This is known as "green hydrogen."
Several challenges need to be addressed before hydrogen can be widely deployed as a net-zero fuel. These include reducing the cost of green hydrogen production, developing and scaling up hydrogen storage and transportation technologies, and expanding the necessary infrastructure. Despite these challenges, hydrogen holds promise as a solution for achieving net-zero emissions. It is a versatile energy carrier that can decarbonize many sectors of the economy, and it can be produced sustainably.
Here are some specific examples of how hydrogen is being utilized to achieve net-zero emissions:
- In Germany, ThyssenKrupp is using hydrogen to produce steel without coal.
- In the United States, Cummins is developing hydrogen fuel cells for heavy-duty trucks.
- In Japan, Kawasaki Heavy Industries is working on a hydrogen-powered ferry.
- In India, the government is investing in green hydrogen production and infrastructure.
These examples illustrate just a few of the ways in which hydrogen is contributing to the goal of achieving net-zero emissions. As the technology continues to advance and the cost of green hydrogen decreases, hydrogen is expected to play an increasingly pivotal role in the global energy transition.
Opportunities for hydrogen sector
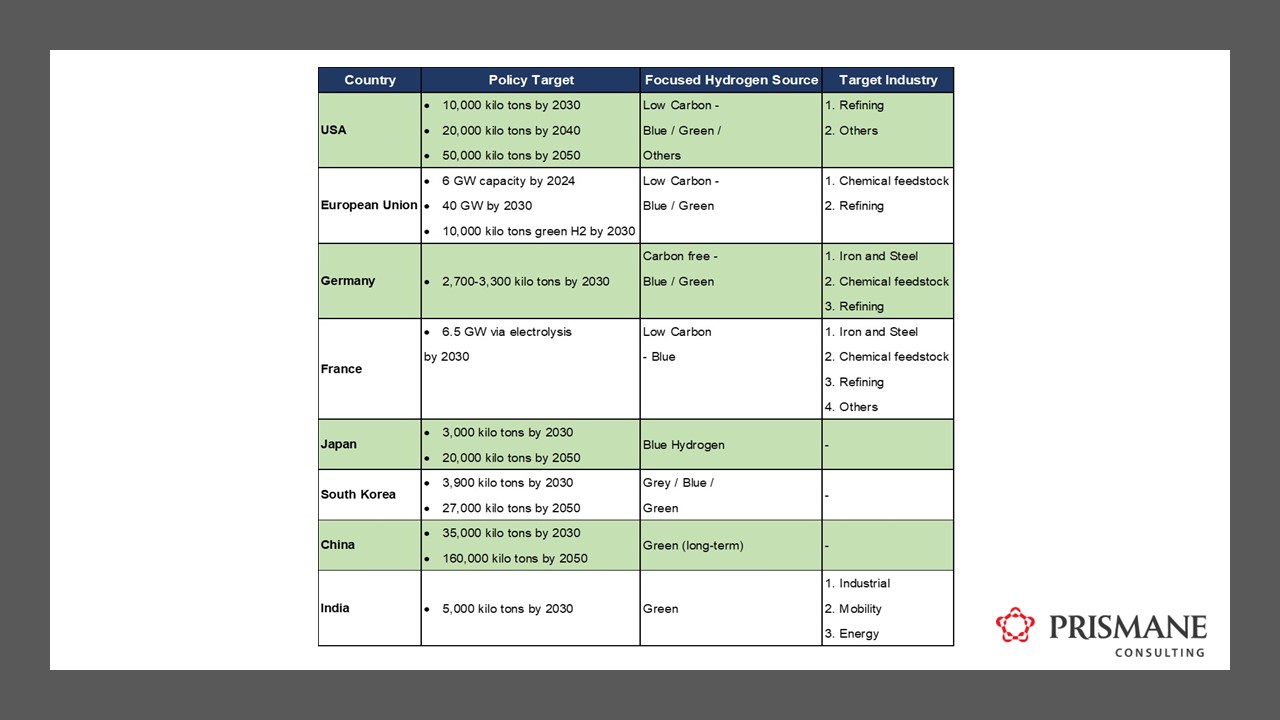
Hydrogen Policy targets
The green hydrogen sector offers numerous opportunities for businesses and investors. Here are a few examples:
Equipment Manufacturing:
The production of green hydrogen necessitates various specialized equipment, such as electrolyzers and fuel cells. There is a burgeoning global demand for this equipment from businesses and governments alike.
Project Development:
Across the world, numerous new green hydrogen projects are in development. These projects present opportunities for businesses to offer services in engineering, construction, and operations.
Investment:
While the green hydrogen sector is still in its early stages of development, it is attracting significant investment. Investors view green hydrogen as a promising opportunity to invest in a clean energy sector with the potential for rapid growth in the coming years.
Here are some specific examples of opportunities in the green hydrogen sector:
- Electrolyzers are the pivotal technology used in green hydrogen production. There is a growing demand for more efficient and cost-effective electrolyzers.
- Green hydrogen production plants can be strategically located near renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind farms, enabling the production of green hydrogen without greenhouse gas emissions.
- Green hydrogen can be stored and transported in various forms, including as a gas, liquid, or solid. Consequently, there is a rising demand for technologies that can safely and efficiently store and transport green hydrogen.
- Green hydrogen finds applications in various sectors, including power generation, transportation, and industry. There is increasing demand for green hydrogen in all these sectors.
- The green hydrogen sector is rapidly expanding with immense potential. Businesses and investors that engage in this sector early on stand to benefit from its growth.
At Prismane Consulting, we have been tracking the hydrogen market for a considerable time and have assisted our clients in meeting their hydrogen market-related requirements.
To Know more please click here
Some of the related studies we have carried out are: